What Is an AI Powered Chatbot? How It Works, Benefits & Use Cases (Case Study)
Visualize a scenario where a Fortune 500 retail company receives 50,000 customer queries every day via email, chat, and social media. The company’s 200-member support staff is on the job 24/7. Yet during peak seasons, the average waiting time for a response is 4-6 hours. Customer satisfaction stays at 72%. The company incurs a hefty $8.5 million cost per year. Then suddenly, they introduce AI chatbots using natural language processing. In just 90 days, waiting time is cut to less than 30 seconds. CSAT is up to 89%. Expenses are down by 43%. The key? Smart automation that is always on.
Chatbot Case Studies show how AI chatbots are transforming the way companies manage customer interactions. Earlier, rule-based systems relied on strict decision trees. Today, AI-based chatbots leverage machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP). They understand context better and continuously acquire knowledge through conversations. Render human-like replies in bulk. Organizations installing these systems experience 62% faster resolution of issues. Engagement rates are 3.5 times higher against basic automation tools. This technical manual illustrates how these systems function. It shows their appropriate timing for deployment. Covers the significant performance metrics from the real world.
What Are AI Chatbots and Why Do They Matter Now?
AI chatbots are AIs designed to interact with humans, either through text or voice. They work very much like a human would. These systems accept natural language input. Understand what the user is looking for. Give a reply that is relevant to the conversation instantly. The main difference between recent chatbot technology and previous versions is key. The latter could only cater to structured types of queries. Meanwhile, the former can understand loose variations of phrasing. Guided by their learning process continuously. This makes them more accurate as well.
Modern-day conversation bots built on artificial intelligence technology use gigantic language models. These models train on trillions of conversational parameters. Additionally, they do so with API integrations with enterprise systems. Have access to customer profiles, product catalogs, and transaction records. This lets them provide users with customized interactions. For example, the retail chatbot might have access to the order status from the ERP system. Checks inventory levels in real-time. Processes returns, all through a single conversation thread. The thread lasts no more than 2 minutes.
The numbers reflect the positive business impact. Companies implementing AI bot technology in conversing see a 40% reduction in support tickets received. Customers solve their problems on their own. As a result, the rate of first-contact resolution goes up by 35%. Productivity of the support team increases by 25%. Workers deal only with hard cases that require human intervention and judging. For a medium-sized firm receiving 10,000 inquiries a month, this means something. It translates to $180,000 savings in labor costs per year. Add in customer retention improvements that can be quantified.
Core Components That Power AI Chatbots
A completely operational AI chatbot system has four technical layers. These layers work in unison. The first layer is Natural Language Processing (NLP). It separates inputs from users into structured data. At the same time, identifies things like dates, product names, and intention categories. A customer submits a text saying, “I want to return my shoes from last week’s order.” Entity extraction activates for product type (shoes), time frame (last week), and action intent (return).
The second layer is the dialogue management layer in Gen AI Chatbot Development. Moreover, it ensures conversation context is retained throughout different turns. It’s also responsible for tracking information already collected. Tracks information still unknown. Determines which business logic should execute next. This is done so the customer does not answer the same questions again. Even multi-step processes requiring customer participation conduct smoothly. Think appointment scheduling or account updates.
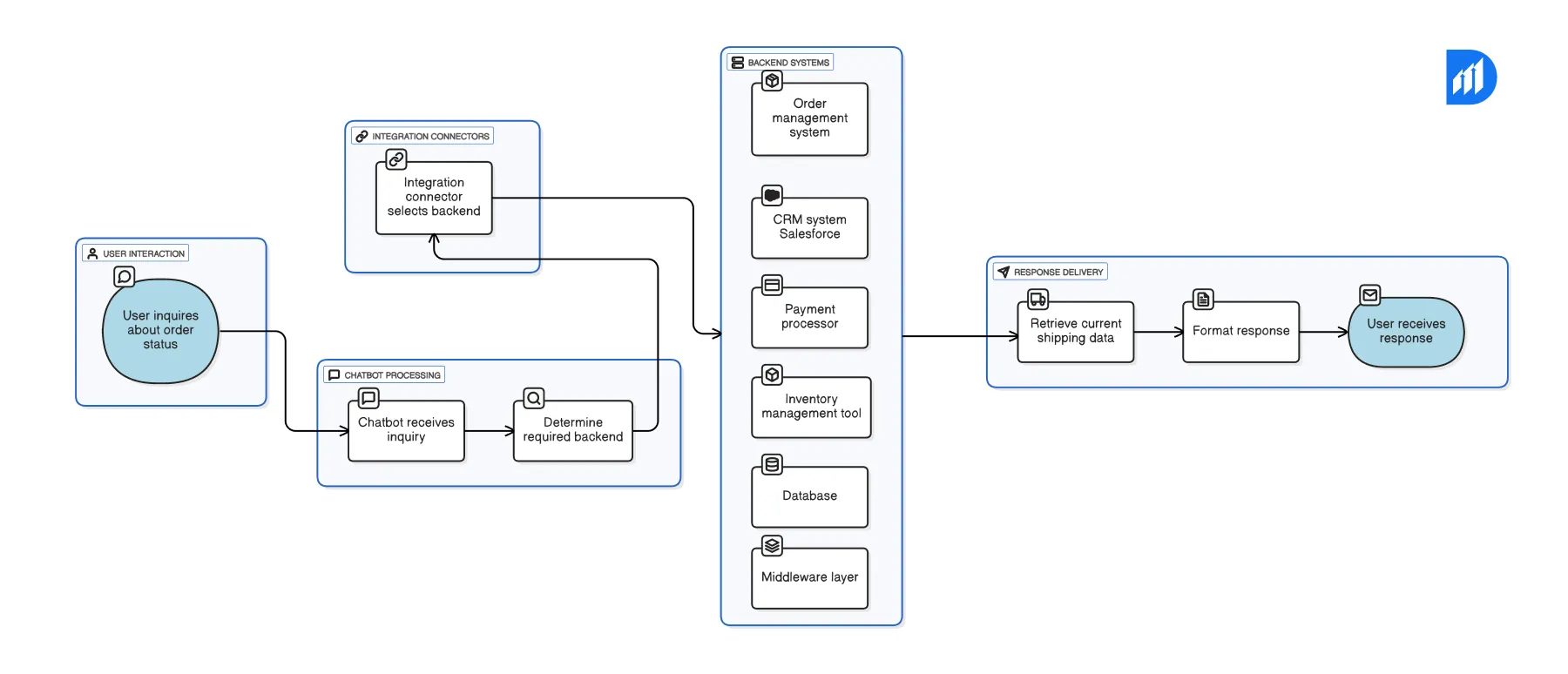
Integration connectors serve as the bridge. Similarly, they connect the chatbot to backend systems. These are typically REST APIs or middleware layers. They access databases. Link to customer relationship management (CRM) systems such as Salesforce. Connect to payment processing companies and inventory management tools. A user inquires about order status. Receives a response over 1-2 seconds. The bot queries the order management system. Retrieves current shipping data. Format the response accordingly.
The response generation layer creates natural language outputs. Cutting-edge systems employ transformer models. Think GPT or BERT. They generate contextually relevant replies conforming to brand voice guidelines. Some deployments incorporate sentiment analysis. A conversation is deemed frustrating. The user is then automatically directed to a human agent.
How Do AI Chatbots Actually Work? Technical Architecture Explained
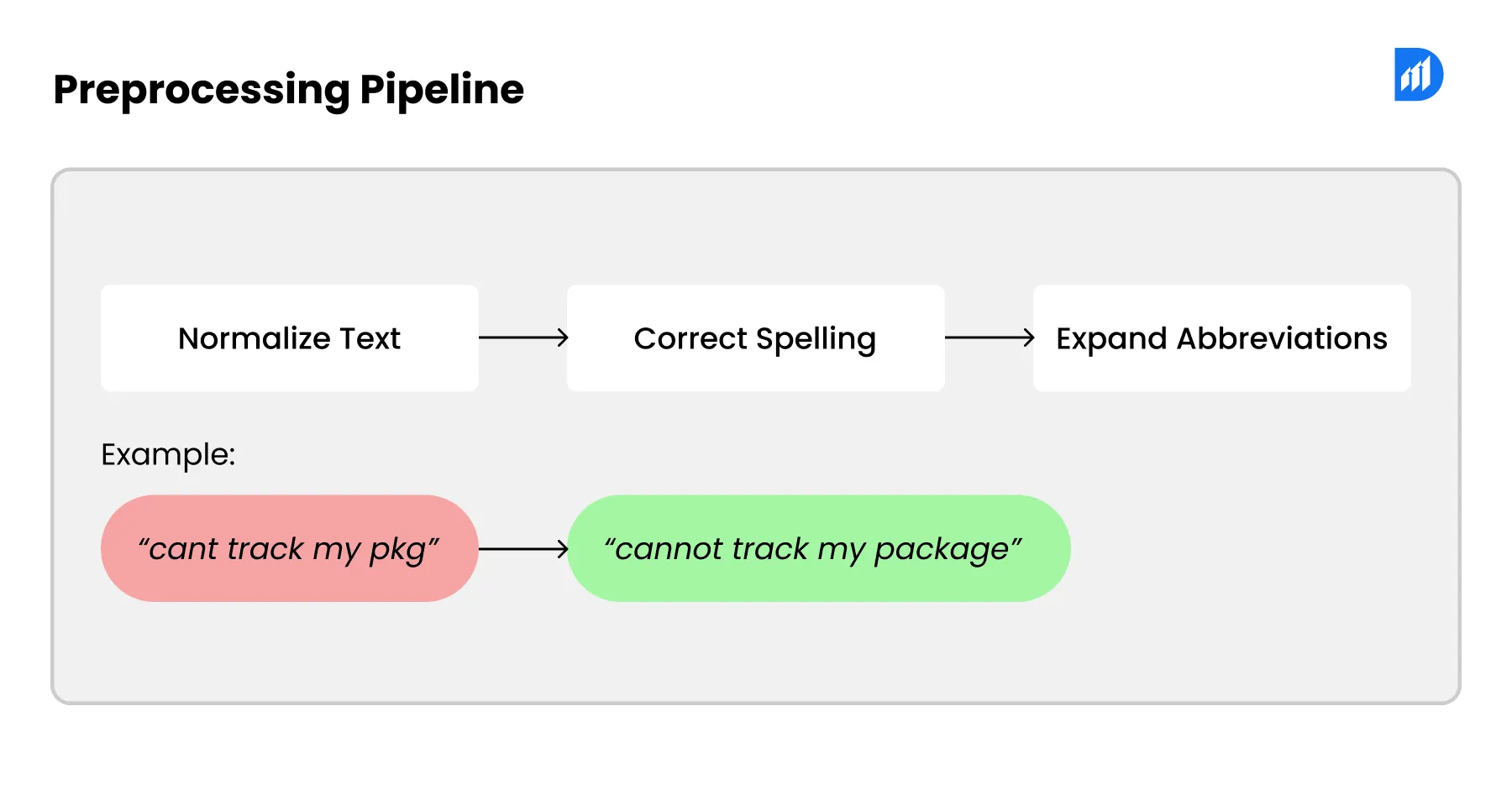
The process flow starts with a user message sent through any channel. It could be a website widget, a mobile app, WhatsApp, or social media. The text input runs through a preprocessing pipeline. It normalizes text. Correct spelling. Take care of any abbreviations. What was previously “cant track my pkg” now changes to “cannot track my package.” Also ready to reach the NLU engine.
Next, intent classification happens. Machine learning models handle this. They train on thousands of labeled examples. In turn, the system predicts the intent for the user message. Produces a score for each intent it recognizes. Think “track_order,” “request_refund,” or “product_inquiry.” When the predicted intent’s confidence score is higher than the predetermined threshold (usually 75-85%), the bot continues with that intent. If confidence scores are fairly low, the bot asks clarifying questions. Or passes the user to a human agent.
Entity extraction operates alongside intent classification. The process extracts particular data points contained in the message. A named entity recognition (NER) model will identify if a message contains a product SKU. Or an order number, a date, or a place. The sentence “Where’s order #12345 going to 10001?” would yield structured parameters. Order_id=”12345″ and zip_code=”10001″ through the entity extraction process.
Dialogue State Management and Context Retention
The dialogue state tracker helps remember the conversation. Session storage supports it. It keeps track of all entities gathered. Tracks the intents established. Monitors the system actions taken during the interaction process. Consequently, the bot can then use this context to bring up earlier messages. Think “As I mentioned earlier about your delivery” or “Regarding the refund we discussed.” This creates an interaction resembling human conversational patterns.
Once the bot collects enough information, business logic execution takes place. This could be making API requests to inquire about order status. Or database searches to get product specifications. Or computation of amounts needing refund based on company return policies. Top-notch AI chatbots perform these operations in the background. This allows continuous conversation flow while processes carry out.
Response Generation Methods
With response generation, the final output is produced. Either using methods based on templates for predictable scenarios. Or generative models for open-ended questions. Templates guarantee consistency for regulated communications. Think about privacy policies or refund terms. Generative approaches handle unique queries not defined in advance. However, these must be strictly controlled to avoid misinformation.
Training AI-powered chatbots needs domain-specific datasets. These comprise actual customer interactions. Development teams annotate thousands of messages. Mark correct intents and entities. Then use these to apply supervised learning algorithms. Models created this way learn associations. Words, phrases, and structures relate to each intent category through various patterns.
Transfer learning makes the process faster. It employs pre-trained language models. Think BERT or RoBERTa. Already know general language patterns. This speeds the process significantly. Fine-tuning these models on a specific company’s data requires only 2,000-5,000 labeled examples. Compare this to 50,000+ for completely starting from scratch. This is the main reason the development process cuts from months to weeks. Retains 85-90% accuracy on intent classification tasks.
Active learning loops upgrade model performance continuously. Pinpoint predictions with low confidence needing human review. If the bot comes across a vague question, flags the interaction. A trainer gives the correct label. Furthermore, the labeled data then merges with the training dataset. In particular, the model undergoes retraining either weekly or monthly. Organizations employing active learning observe an accuracy increase. Gain 12-15 percentage points within the first half year of deployment.
When to Deploy AI Chatbots vs. When Not To
AI chatbots suit certain situations well. Volume is high. Query nature is semi-structured. Fast response is crucial. Customer service teams handle repetitive questions. Think hours, locations, policies, or account status. They will benefit immediately. E-commerce sites have thousands of product inquiries. See 35-40% deflection rates. Customers receive instant answers without waiting for agents.
AI powered chatbots have become so common. Online financial services firms made them their first line of communication. These chatbots take care of account inquiries. They offer transaction history. Help with basic problem-solving. Medical professionals use the same tools. For appointment making. For prescription renewals. For symptom checking. All this while staying within HIPAA regulation limits. The common traits among these use cases stand out. All have well-defined areas. Sources of data are structured. Metrics are tied to efficiency gains. Easy to measure.
When Chatbots Don’t Work
Nonetheless, instances exist where ai chatbots still do not perform well. Or cause negative user experience. For example, negotiations are complicated. Need judgment calls. Think contract terms, secretary pricing exceptions, or escalated complaints. Certainly require human expertise to solve them. Moreover, situations are highly emotional. Crisis support or very personal issues matter here. The current AI might not provide empathy and nuance a human would. Therefore, deploying bots in these areas may result in customer dissatisfaction. Harm could be done to the brand.
Furthermore, technological limitations contribute to the problem. Organizations have data quality issues. Uncoordinated systems exist. Vague business processes remain. They find it extremely challenging to build functional chatbot applications. If the human agent cannot quickly obtain accurate information, the bot faces the same problem. Companies should first deal with these foundational issues. Do this before attempting AI deployment. Otherwise, might implement technology that only worsens existing problems instead of solving them.
Decision Framework for Chatbot Deployment
Before allocating resources, review deployment readiness in four aspects. Volume of queries and repetitions justifies the investment. If fewer than 500 inquiries in a month follow similar patterns, traditional support channels would still be more cost-effective. Availability of data is a decisive factor. Determines what the bot can really do. If customer records and product information are not easily accessible, responses will be generic. Not very helpful.
User expectations matter greatly. Chatbots are easily accepted by people open to self-service and digital channels. However, the group preferring human interaction might be reluctant. User acceptance testing via small pilot programs discloses adoption patterns. Do this before complete launch. One healthcare system reported 78% patient satisfaction with the ai conversation bot for scheduling appointments. But only 34% for medical advice. This data was the basis for developing their bot deployment strategy.
Integration complexity determines time to get value. Rapid bot implementation happens with platforms having strong APIs and modern architectures. Meanwhile, legacy systems need custom middleware or manual data entry. Require a time extension from weeks to months. When comparing chatbot options, consider the total cost of ownership. Include integration work, maintenance, and model retraining.
Key Benefits That Drive AI Chatbot ROI
Operational cost reduction will be the most direct and instant financial impact. AI chatbots manage 60-70% of tier-one inquiries without involving humans. Companies can grow work volume without increasing employee numbers proportionally. A telecom company handles two million calls a month. Reduced human agent interactions by 1.3 million through conversational AI use. This saved $4.2 million per year in labor costs. All while still meeting service quality metrics.
Availability and consistency in quality contribute to increased customer satisfaction. Instant response times of 5 seconds or less match digital channel expectations. Customers demand the service there. Additionally, the most advanced ai chatbots are always on. No matter the time zone their users are from. Eradicate hold times. Remove business hour restrictions. Customer feedback during and after interaction shows results. Accordingly, the satisfaction rate for bot-resolved issues is 83%. Compared to 79% for human-resolved cases in uncomplicated situations.
Scalability across the board during demand spikes proves to be a major factor. Shows business resilience. Events like Black Friday traffic, product launches, or crises can easily burden traditional support teams. Notably, with generative ai services, chatbots process up to ten times the usual query volume. No loss in quality occurs. Keep the same response times. Human teams would face multi-hour waits otherwise. Consequently, this superb capacity protects revenue during critical sales periods. Also retains customers who might otherwise leave due to service disruption.
Data Collection and Performance Insights
Data collection and insights are secondary benefits coming along with primary ones. Each and every chatbot interaction produces structured data. Concerns customer needs, problems, and behavior patterns. Apart from that, analytics can show products leading to most questions. In particular, the stages in user journeys where users drop out. Equally important, the areas of confusion created by policies. Product development teams most often get benefits from this intelligence. Improve their offerings. Operations optimize processes based on actual friction points instead of assumptions.
Companies successfully implementing this technology quantify its value. Through direct optimization tracking specific KPIs. Resolution rate is an indicator. Shows the percentage of conversations completed without needing human escalation. Targets are usually set at 65-75% for mature deployments. Containment rate monitors issues solved entirely by the bot. Compare to those requiring agent transfer. Higher percentages signify better training and integration.
User satisfaction scores derive from post-chat surveys. They provide direct feedback on experience quality. Over 80% scores indicate the bot is meeting customer needs. Ratings below 70% are considered indicative of problems. Either accuracy problems or friction points needing address. Keeping track of satisfaction according to intent category will expose specific workflows. These require improvement rather than making blanket statements about performance.
Cost per conversation measures financial effect. Commonly divide operating costs of the chatbot by the number of monthly interactions. This ratio makes comparison with human agent cost easy. That is between $6 and $12 for a single contact. AI chatbots reduce the cost down to $0.50-$1.50 per conversation. Means around 75% to 90% cost savings if used on a large scale. To calculate total savings, multiply the cost difference by the number of resolutions.
Real-World Case Study: Retail Transformation Through AI Chatbots
A national retailer with 400 stores and $2.8 billion in annual revenue experienced significant customer service challenges. Their customer service center received 45 thousand weekly inquiries. Channels included phone, email, and chat. There were 180 agents working full-time. In particular, the average email response time was 8 hours. For chat during peak times, it was 12 minutes. Customer satisfaction rating was at 68%. First-contact resolution was only 52%. Meanwhile, the company incurred an annual support cost of $9.2 million. Was increasing at 18% every year. Sales volume was going up.
Implementation Overview
The retailer adopted AI-powered chatbots. Integrated with their Salesforce CRM and order processing system. The whole process took 12 weeks. It included mapping out user intents, connecting systems, and training agents. Focused on five areas with most impact. Order tracking. Return policy. Store hours. Product availability. Account management. Those five categories accounted for 62% of total inquiry volume. Based on six months of historical data.
Technical Infrastructure and Implementation
The technical infrastructure included machine learning models for natural language processing (NLP). Built on 8,000 customer interactions labeled for training purposes. Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) connected to three backend systems. Subsequently, deployment happened across website, mobile app, and Facebook Messenger. One continuous service. Initially, the chatbot gathered customer data. Then checked the order in real-time. Provided tracking links. Or started return cycles within a conversation lasting 90 seconds.
Escalation to human agents took place seamlessly. Sentiment analysis pointed out frustration. Or intent detection exceeded trained categories. Notably, the outcome after 90 days was better than expected. Every metric improved. In particular, the chatbot was responsible for 28,000 weekly conversations. Resolution rate was 71%. As a result, human agents got 19,880 fewer inquiries to handle. Average resolution time for bot-handled cases reduced to just 45 seconds. Customer satisfaction scores for automated interactions were 86%. That was 8 points higher than scores of human agents. Overall first-contact resolution rate raised to 73%. In essence, the bot gave instant answers to common questions.
Financial Impact and ROI Analysis
Financial impact also showed clear ROI in the first quarter. Lowered agent workload enabled the firm to shift 40 positions. They went to complex issues handling and proactive outreach. Not backfilling attrition. Overall, savings in labor costs came to $1.8 million per annum. Notably, the chatbot implementation cost was $185,000. Included software licensing, integration of work, and training. That is a payback period of less than 8 weeks. The projected savings for three years are $5.4 million. Against $320,000 in ongoing operational costs.
Key Success Factors
The deployment brought about various critical success factors. Initial intent selection targeted high-volume and low-complexity scenarios. This allowed for fast wins and user acceptance. Starting with order tracking helped. Essentially, the only highest volume category at 18,000 weekly inquiries. Gained confidence before going into more complicated intents. Think product recommendations.
Integration quality was a bigger factor in user experience than NLP accuracy. Users still got frustrated with the bot. Even with its 90% intent classification accuracy. Could not support the functionality. Real-time order data was unavailable due to API limitations. Therefore, the team took backend connectivity as the priority. Over new intents. Ensured every supported use case worked perfectly. Before expansion of scope.
Training did not stop. Continuous training proved crucial for performance maintenance. Specifically, the retail team went through conversations. About 500 randomly picked customers per week. Came up with new phrases. Identified entity types. Spotted edge cases. Monthly retraining of the model used these. Gave a boost to accuracy. From 82% at launch to 91% after six months. Active learning lessened annotation burden. By only automatically flagging ambiguous interactions. Not having to review all conversations.
Choosing the Right AI Chatbot Platform for Your Business
Platform assessment starts with listing technical needs. In terms of integration, deployment, and functionality. Businesses already having CRM systems such as Salesforce or Microsoft Dynamics should give priority. To vendors with native connectors. These automatically sync customer data. Furthermore, custom integration through REST APIs is still an option. But the implementation timeline gets extended by 4-6 weeks. Compared to pre-built connections.
Channel requirements will alter platform choice very much so. Companies aspiring to have an omnichannel presence need consideration. Across web, mobile, SMS, WhatsApp, and social media. Require platforms facilitating multi-channel deployment from one bot definition. This unified approach not only keeps logic and training consistent. Across different channels. But also allows for specific adjustments for each channel. Think character limits or rich media support.
Customization vs. Ease of Use
The trade-off between customization capabilities and ease of deployment represents a key consideration. Low-code platforms such as Chatfuel or ManyChat allow for quick deployment. With visual interfaces. Yet, they do not support complex rules. Do not allow for deep integrations at the same time. On the other hand, enterprise platforms like IBM Watson Assistant or Google Dialogflow provide extensive customization. Through APIs and webhooks. But can be resource heavy. In terms of developer capacity. Adjust the platform’s complexity. According to your technical team’s skills and use case requirements.
Analytics and Enterprise Considerations
Analytics and reporting features support continuous improvement process. Platforms offering conversation logs should be sought after. Along with intent confidence scores. Entity extraction accuracy. User satisfaction metrics in real-time dashboards. Business intelligence tools can be used for deeper analysis. Thanks to export capabilities. A/B testing frameworks to compare variations in responses matter. Thus optimize conversion rates. Part of the best platforms.
The main focus of enterprise implementations is security, compliance, and scalability. Major healthcare providers will only use HIPAA-compliant platforms. With encryption at rest and in transit. Plus audit logging. Access controls. Similarly, financial institutions will also require similar protective measures. Under PCI DSS standards. Wise to check vendor certifications. Before allowing chatbot interfaces to handle any sensitive customer data.
Scalability testing plays an important role. In keeping performance issues at bay under heavy traffic. Latency degradation should not be an issue. Enterprise platforms can support over 10,000 simultaneous conversations. When load testing is done during system implementation, bottlenecks can be detected early. Mainly due to third-party APIs or database queries. Would certainly help to avoid creating poor experiences during production load. Cloud-based infrastructure with auto-scaling can effectively manage growing usage. Without any limits on capacity.
Consumer-Focused Solutions
User experience and fast deployment are the main priorities. Of consumer-focused platforms. Rather than enterprise features. For basic customer service, a small business using AI chatbots online may find consumer platforms sufficient. Think Tidio or Landbot for their needs. Solutions are characterized by less customization depth. To provide quicker setup and cheaper price. The right tradeoff. When dealing with simple use cases that do not involve sensitive data.
Implementation Roadmap: From Planning to Production
A successful deployment follows a structured methodology. Start by defining the use case and agreeing on scope. In addition, customer service, IT, and business leadership should all be on the same page. Regarding the queries the bot will handle. Success metrics. Timeline expectations. Document current state metrics. Average handle time. Resolution rates. Customer satisfaction. To establish baseline for measuring improvement.
The majority of time-consuming processes in early phases are intent mapping and collecting training data. Look back 3-6 months at customer interactions. Check their patterns and frequency to sort them out. Map the inquiries to possible intents. Essentially, the goal being 10-15 categories representing 70-80% of volume. For each intent, collect and label 100-200 examples. For initial training of the model. Make sure there is diversity in phrasing. Cover the edge cases.
The technical architecture design deals with system integration. Along with data flow. Security requirements. Essential to indicate backend systems the bot must access. And the information that should be exchanged. Consequently, API specifications should include authentication. Rate limits. Error handling. Conversation flow diagrams should depict decision points. Data collection steps. Handoff triggers.
Development, Testing, and Launch Phases
Development and testing phases allow to build the chatbot. Plus integrate systems. Validate performance. In development environments, possible to test conversation flows. Without affecting production systems. User acceptance testing should be done internally. By teams who play customer roles. To spot logical gaps or awkwardness in phrasing. Feedback should be the basis for iteration. Until external launch.
A pilot launch with limited user exposure is a way to validate. In the real world before full deployment. About 10-20% of traffic will be directed to the chatbot. While human agents will be available for escalations. In the meantime, performance metrics will be monitored daily. Adjusting confidence thresholds and training data as needed. User feedback will be collected through post-conversation surveys. To highlight friction points.
Continuous Optimization
The optimization of AI chatbots performing well never ceases. Weekly review cycles will be established, specifically to look into conversation logs, escalation patterns and user satisfaction scores. Notably, new intents coming from unhandled queries will be identified. Categorized according to volume. Retraining of the model every quarter will include collected training data. Thus, improving accuracy by 2-4 percentage points per cycle.
Keeping content up to date is necessary. To ensure information is correct as company policies, products, or services change. Therefore, create change management procedures. That makes it a requirement for the chatbot’s knowledge base to update. At the same time with website content or policy changes. When the bot’s answers do not match actual policies, bad customer experience results. Increasing the number of calls to agents.
Trying different styles of A/B testing helps. Conversation flows. Escalation points. Will discover where optimization is possible. Accordingly, use a strong statistical approach. To verify changes based on hypothesis. Does a friendly tone bring more satisfaction? In contrast to a concise one? Will shorter dialogues or longer explanations lead to better resolution? Decisions made based on data are more effective. Then those made based on assumptions. When it comes to user experience optimization.
FAQs
What is an AI chatbot, and how is it different from traditional chatbots?
AI chatbots benefit from machine learning and NLP. Traditional ones are rule-based and only capable of following decision trees and scripts.
How do companies assess the performance of their AI chatbots?
Primary indicators include resolution rate (65-75% target), customer satisfaction rating (80%+ goal), conversation cost, and rate of customers not requiring human intervention.
Which sectors are most likely to derive benefits from AI chatbots?
Retail, finance, healthcare, and telecommunication get the best ROI. High inquiry volumes, repetitive questions, and clear efficiency metrics drive success.
Can AI chatbots work together with the business systems already in place?
Yes, latest platforms plug into CRM systems, order management, and databases via REST APIs for real-time data access during chat.
How long does it take for companies to deploy an AI chatbot?
Standard implementations typically take 8-12 weeks from planning to launch. Complex deployments in large companies take 16-20 weeks with multiple integrations.





