Ecommerce vs Retail Store: Key Differences, Benefits, and Business Impact

The current disagreement between ecommerce vs retail store shopping has expanded beyond its original scope because it now relates to technological infrastructure systems. A Shopify ecommerce platform which serves mid-sized businesses handles thousands of daily transactions while executing three critical functions. The operation of all three systems has reached a point of increased efficiency as their performance gap continues to expand. Retail establishments which follow the traditional model need their employees to conduct inventory assessments when business hours conclude. The performance gap between these two models is widening fast.
Statista reports that worldwide ecommerce sales reached 5.8 trillion dollars in 2023 which will exceed 8 trillion dollars by 2027. That growth is not just consumer preference. The new business environment requires organizations to build their operational models. Organizations today need to manage enormous data while maintaining their ability to deliver actual value to customers which creates a challenge that seems simple yet remains difficult to achieve. The gap between two business outcomes which decision-makers need to understand when they evaluate ecommerce tools and digital transformation solutions holds the key to assessing their value for their organization.
What Is Ecommerce Architecture, and How Does It Differ from Traditional Retail Store Infrastructure?
Ecommerce architecture stands as the complete system which powers online shopping while maintaining distinct boundaries from traditional retail systems. The complete ecommerce system consists of front-end display elements, back-end operational functions, payment processing systems, inventory control systems, order fulfillment systems, and cloud computing resources. The core structure of this system operates through platforms like Shopify, WooCommerce, Magento, and BigCommerce.
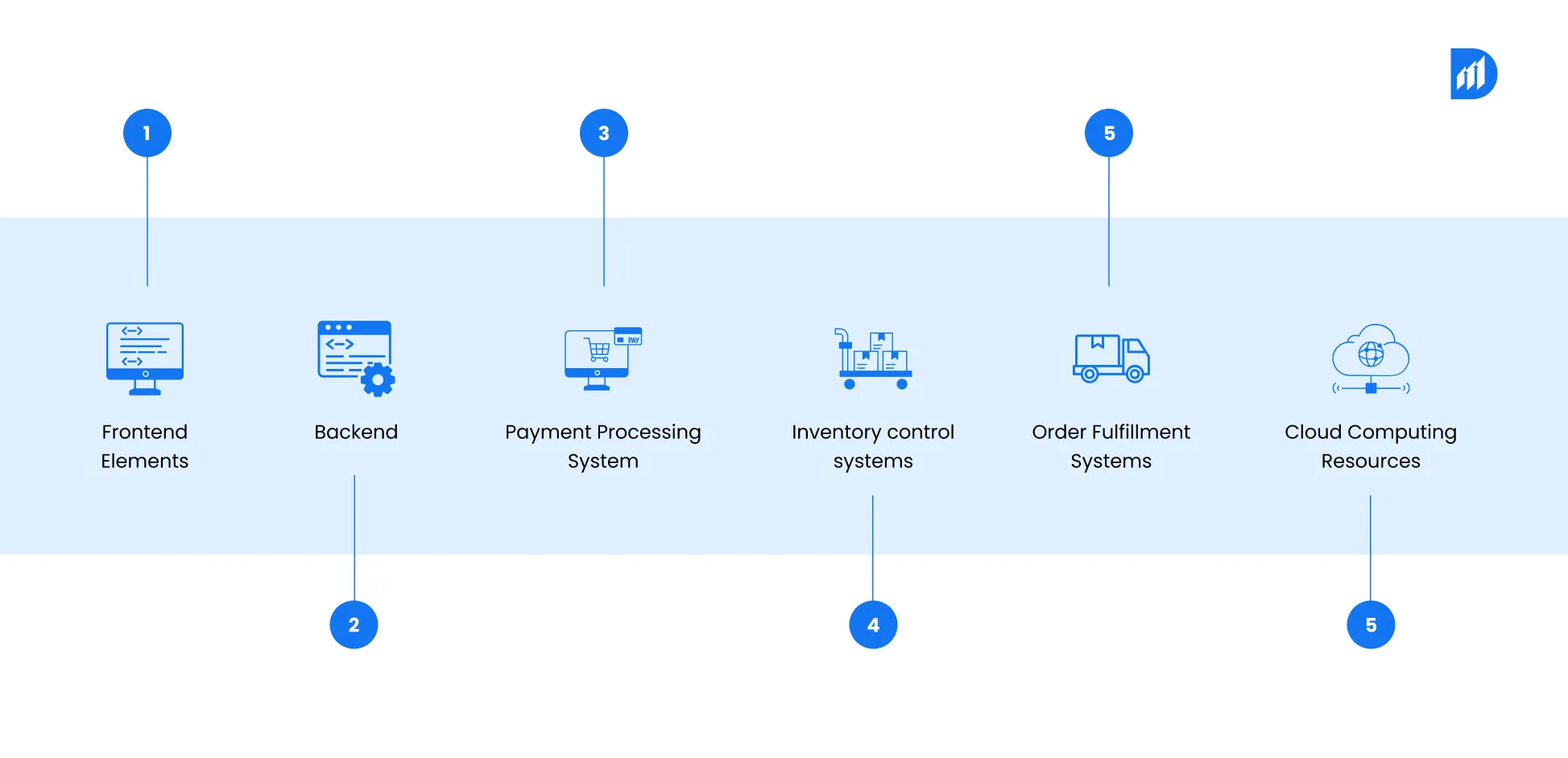
The infrastructure of traditional retail stores depends on physical point-of-sale terminals, local servers, in-store Wi-Fi networks, and manually operated inventory systems. Most legacy retail setups were not originally designed for real-time data processing. The system operates with batch-refresh cycles which results in data becoming outdated for several hours before managers can utilize it.
Ecommerce platforms of today implement microservices architecture which allows each function to operate as a separate service. Developers now have the capability to modify the payment system without impacting the product catalog. Retail stores which operate monolithic legacy systems face permanent operational halts and high expenses when they try to implement this solution.
How Do Ecommerce Platforms Compare with Brick-and-Mortar Retail Systems in Digital Capability?
The gap in digital capability between ecommerce vs retail store setups is measurable. Shopify ecommerce platform detection methods, for instance, allow businesses to analyze competitor storefronts through metadata headers, robots.txt patterns, and script libraries. Shopify ecommerce platform identification methods also help brands benchmark their own tech stack against competitors. Traditional retailers face a complete lack of digital intelligence because they require extensive financial resources to achieve this capability.
The following comparison highlights key capability differences between modern ecommerce platforms and brick-and-mortar retail systems:
| Capability | Ecommerce Platform | Traditional Retail Store |
| Real-time Inventory | Yes (cloud-synced) | No (batch refresh) |
| Customer Data Collection | Automated + AI-driven | Manual or limited POS |
| Personalization Engine | AI-powered | None |
| Scalability | Instant (cloud) | Physical expansion required |
| Order Fulfillment Speed | Automated 3PL ecommerce fulfillment | Manual warehouse picking |
| Analytics Dashboard | Live dashboards (Power BI / GA4) | End-of-day reports |
Ecommerce consulting firms report that retailers which implement platform-level digital technologies achieve a 30 to 40 percent decrease in operational costs during their first operational year.
What Are the Core Technology Differences Between Ecommerce and Physical Retail Operations?
The basic technological elements which define digital commerce and physical store operations show their primary distinctions in operational execution. The ecommerce platform uses cloud-based technology to operate its complete technology stack. Kubernetes handles containerized applications. Apache Kafka manages event streaming for real-time order tracking and inventory sync. The product search system uses either Elasticsearch or Algolia to deliver results within 100 milliseconds of search execution regardless of catalog size.
Physical retail stores need dedicated on-site systems to operate. Traditional point of sale systems connect to nearby servers which then transmit data to the main ERP system after predetermined times. A single system breakdown can bring down all store functions. Major investment is required to achieve automatic scaling, system redundancy, and immediate failure notifications.
Speed is where the difference becomes most critical. The ecommerce platform completes payment operations within 2 seconds. Traditional retail needs customers to interact with physical devices while staff performs manual card checks and customers receive printed receipts.
How Does Ecommerce Leverage Cloud Computing, AI, and Automation Compared to Retail Stores?
The ecommerce industry depends on cloud computing services to achieve required scalability. Shopify automatically increases its infrastructure capacity during peak shopping times such as Black Friday to support millions of users simultaneously. Both AWS and Azure provide AI and ML services which ecommerce platforms use to create dynamic pricing systems, fraud protection mechanisms, and customized user recommendations without needing to develop their own models.
Physical retail stores have faced challenges when trying to implement AI technologies throughout their entire operations. Machine learning models need cloud access to obtain real-time data streams which enable their operation. Modern retailers use AI-driven cameras to track customer movements while smart shelf sensors detect stock shortages. The systems operate as additional tools which do not serve as essential elements of their infrastructure.
The ecommerce industry shows its advantages through automated systems. AI Marketing Agents now perform customer segmentation and A/B testing operations together with campaign execution tasks without needing any human input. Ecommerce brands conduct their marketing efforts through multiple tailored campaigns which run simultaneously across their business operations.
How Do POS Systems, ERP, and CRM Integrations Differ in Ecommerce vs Retail Environments?
The POS system operates completely through digital processes in ecommerce environments. It captures order data, payment information, and customer details simultaneously. This data automatically transfers to both ERP and CRM systems using API integrations which establish a common data framework. Salesforce, HubSpot, and Microsoft Dynamics all offer native connectors to Shopify and Magento.
The original design of conventional retail point-of-sale systems was to handle financial transactions, while their later function as data intelligence systems remained secondary. Sometimes a simple sale ends up taking hours because the data is just… sitting in one system before moving to another, and meanwhile teams are manually updating CRMs like it’s 2012.
And then the smallest integration gap decides whether loyalty programs and omnichannel shopping feel smooth to customers or start glitching right at peak time.
How Does Data Analytics and Customer Intelligence Vary Between Online and Offline Retail Models?
Ecommerce platforms create massive amounts of user tracking information which includes data on click paths, session length, cart abandonment, buying habits, and device usage. This data gets processed through Google Analytics 4, Mixpanel, and Amplitude which generate usable insights within minutes.
Physical retail environments gather much less information, and the data they do obtain comes to them after considerable delays. McKinsey reports that data-driven organizations show 23 times better customer acquisition rates and 6 times better customer retention rates. Retailers without real-time analytics make decisions based on yesterday’s numbers, which compounds errors over time. The AI and ML Solutions available today give ecommerce platforms a clear customer intelligence edge. Amazon’s product recommendation systems generate up to 35 percent of their total sales through algorithmically recommended products. The requirement for highly skilled sales personnel in retail stores exists because these employees are essential for achieving sales results that match those achieved by other stores.
What Role Does Cybersecurity Play in Ecommerce vs Traditional Retail Systems?
Cybersecurity needs differ substantially between ecommerce vs retail store systems. Ecommerce platforms process payment card data, personal identifiable information, and behavioral data at massive scale. The platforms need to follow requirements from PCI DSS, GDPR, and regional data protection laws. Merchants achieve Level 1 PCI compliance through Shopify which handles security requirements for them.
Ecommerce businesses face unique identity verification security risks. An AI-Powered Video KYC Platform can verify customer identities during account creation or high-value purchases in under 60 seconds. The system replaces manual document verification while decreasing fraudulent account creation by 70 percent according to industry standards.
Physical security threats for traditional retail stores include shoplifting, employee theft, and vulnerabilities related to cash handling. The number of digital threats facing retailers has decreased but is increasing as they implement connected devices, self-checkout kiosks, and loyalty app integrations. Retail businesses now face growing attack surfaces because their security systems have not expanded to handle this increase.
How Do Scalability and Digital Infrastructure Impact Ecommerce and Retail Business Growth?
The decision to expand an ecommerce business depends primarily on software and infrastructure choices. The system needs only days to create new markets together with product lines and sales channels. Businesses can use cloud platforms such as AWS and Azure to launch their services throughout different regions while delivering quick worldwide response times. A brand selling in the US can add European operations without opening a physical office.
Retail expansion needs a big investment of financial resources. Each new store requires real estate acquisition, personnel recruitment, inventory procurement, and local compliance management. The average cost of opening a new retail location in the US ranges from $50,000 to $500,000 depending on the industry. Ecommerce businesses reach new geographies for a fraction of that cost.
Digital infrastructure also impacts uptime. Ecommerce platforms operate with a goal of 99.99 percent uptime which allows for less than 53 minutes of downtime each year. Physical retail stores need to shut down because weather conditions and power failures and staffing shortages create problems that exceed standard infrastructure capacity.
How Does Omnichannel Technology Bridge the Gap Between Ecommerce and Retail Stores?
The most effective retailers no longer choose between ecommerce vs retail store models. They build omnichannel systems that unify both. BOPIS which stands for buy online pick up in store received a 208 percent increase during 2020 and remains a popular shopping method today. This model needs both online and physical store systems to share inventory information in real time.
The implementation of omnichannel retailing depends on RFID tagging technology, cloud-based inventory systems, and headless commerce design frameworks. Stock prediction methods that operate across different channels use AI and ML solutions for inventory forecasting. Without this accuracy, businesses will lose customer trust because online stores will sell out while physical stores lack sufficient stock.
Unified commerce platforms like Salesforce Commerce Cloud and Oracle Retail provide businesses with a unified customer profile system. This enables tracking of customer actions across all online and offline interaction points. Businesses get complete customer information which they can use to deliver more accurate marketing and improved customer support during any sales interaction.
What Are the Technology-Driven Business Benefits of Ecommerce Compared to Retail?
The performance data which businesses use to evaluate ecommerce vs retail store operations shows clear results. Ecommerce companies experience 60 percent reduced customer acquisition expenses when they use AI-based digital marketing instead of traditional retail advertising methods. Businesses also achieve lower operational expenses because they avoid rent costs, need fewer employees, and use 3PL ecommerce fulfillment partners to process orders automatically.
Ecommerce reduces the time needed to develop new products. AI in Product Development enables rapid prototyping and demand forecasting which leads to 40 percent faster product delivery. Physical retailers need to schedule their manufacturing operations several months ahead which creates inventory risks that ecommerce businesses avoid through just-in-time inventory delivery systems.
The retail performance metric of revenue per square foot has lost its value as a measurement tool. Ecommerce replaces it with revenue per acquisition cost and lifetime customer value. These are two metrics that grow without physical limitations. Businesses which compare their online earnings to their in-store earnings observe that ecommerce profit margins increase annually because technology expenses decrease. The profit margins for many businesses online vs. offline show a clear longstanding trend in favor of e-commerce.
How Can Businesses Use Digital Transformation to Optimize Ecommerce and Retail Strategies?
Digital transformation is not about choosing ecommerce over retail. The process requires organizations to establish a technological base which improves performance through both ecommerce and retail channels. AI and ML capabilities, which connect ERP systems with CRM platforms and commerce systems, enable organizations to create data loops which improve customer experience and operational efficiency through ongoing enhancements.
The first real step for any business starting this journey is honestly just fixing the data foundation. Once everything sits in one place through unified platforms like Databricks or Snowflake, sales data from all channels finally starts making sense instead of living in ten different spreadsheets. Machine learning models can then detect customer behavior patterns which remain hidden when different channels operate separately.
Ecommerce consulting services play a key role here. Consultants identify current technology deficiencies, select suitable platform combinations, and develop migration plans which ensure operational continuity. The goal is not to build technology for its own sake. The main objective requires creating systems which deliver measurable results for both online and offline retail operations.
When Ecommerce Alone Is Not the Right Answer
Not every business is best served by a pure ecommerce model. Physical retailing offers better results for high-touch products which need customer consultation, luxury goods, medical devices, and custom-fit products. Customers who buy products worth over $1,000 demonstrate 60 percent higher conversion rates when they test the product before purchasing.
Businesses operating in markets where people use the internet less and make cash payments more need to use physical stores as their main selling method. Ecommerce tools provide solutions for numerous challenges but their operational capacity does not match the ability of physical stores to build trust, show products, and give immediate satisfaction to customers who need those services.
Final Thoughts
The ecommerce vs retail store debate has moved beyond consumer preference into enterprise technology strategy. Businesses that achieve success today do not select between two operational models. They employ technology to enhance both which enables better data sharing and improved customer service.
Durapid Technologies empowers businesses to construct AI and cloud systems which create the data infrastructure needed for digital transformation. Our team of 120+ certified cloud consultants and 95+ Databricks specialists has successfully handled projects which include migrating legacy retail systems to the cloud, integrating ecommerce platforms with ERP, and deploying machine learning models for demand forecasting.
Discover how Durapid’s AI and ML Solutions enable your business to enhance its ecommerce results through improved physical retail operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main technical difference between ecommerce and a retail store?
Ecommerce uses cloud-native API-based systems which process data instantly while traditional retail uses on-site POS systems which handle data updates through scheduled intervals leading to decision-making delays.
How does the Shopify ecommerce platform differ from retail store management software?
Shopify provides a comprehensive software-as-a-service platform which enables users to handle payments and inventory management and order fulfillment and marketing activities through a unified system. The standard retail management system provides basic POS and inventory functions which necessitate additional software solutions for customer relationship management and marketing activities.
What ecommerce tools give online stores an advantage over physical retail?
Ecommerce operations use AI-based recommendation systems, real-time analysis dashboards, automated 3PL ecommerce fulfillment systems, A/B testing systems, and digital marketing automation platforms to achieve results which physical stores cannot provide at similar expenses.
Do businesses make more profit online vs in-person?
Online businesses typically show higher margins due to lower overhead but profitability depends on customer acquisition costs and product type. High-ticket, high-touch products usually generate higher profits through physical stores which have better conversion rates.
What role does ecommerce consulting play in bridging ecommerce and retail operations?
Ecommerce consulting helps businesses discover platform deficiencies, create omnichannel technology systems, and connect online platforms with physical store operations. Consultants help businesses avoid expensive platform errors while speeding up the process of creating business value.





