AI in Product Development: How Smart Teams Ship Better Products 3X Faster

After an eight-month period of conducting customer surveys and seeking stakeholder opinions, the product team of your company has just finished building a feature. You are confident of the launch. However, within a short period of two weeks, only 4% of the customers have adopted it. Support tickets have increased by 67%. At the same time, your rival who is applying AI in product development has conducted an analysis of 2.3 million user interactions. They pinpointed the real problem, built the solution in six weeks, and even taken 28% of your target market before you figured out what had gone wrong.
Such a situation is no fiction. AI-powered product development cycles report 3.2 times faster time-to-market. Nearly half of the product launches avoid failure compared with traditional ways. The difference between AI-supported teams and conventional methods is not only growing but also becoming existential. Companies that do not adapt AI in product development end up with R&D costs 40% more and with 60% less innovations ready for the market.
What Is AI in Product Development and How Does It Change the Way Modern Innovation Works?
AI in product development is the use of machine learning algorithms, natural language processing, computer vision, and predictive analytics in a practical and systematic way throughout every product development stage, from concept to market. In contrast to old development methods that depend on customer feedback and manual analysis at intervals, AI product development develops continuous feedback loops. These loops analyze millions of data points in real-time to guide design choices.
The change is noticeable on four major fronts. Firstly, AI removes uncertainty from the idea generation process. It predicts feature adoption rates with an 89% accuracy through thorough market trends, competitor positioning, and user behavior pattern analysis. Secondly, it cuts design iteration cycles down from weeks to hours. Generative design algorithms generate thousands of potential prototypes based on given limits. Thirdly, AI-based testing environments can mimic years of user interactions in just a few days. This uncovers the rarest of cases that human testers usually miss in 73% of the cases.
In product development, the traditional approach is linear: research, design, prototype, test, manufacture, launch. With AI in the picture, teams transform this into a parallel, iterative process. All stages happen at the same time. For example, while designers make mockups, AI processes real-time user feedback on similar products. Engineers build prototypes while machine learning models anticipate manufacturing problems. Marketers figure out their campaigns while natural language processing tools conduct sentiment analysis on 47 social platforms to sharpen the messaging for launch.
Which Core Technologies and Capabilities Define AI-Driven Product Development?
AI product development incorporates six basic technology layers. These layers provide the required features and make intelligent development environments possible. The analytical backbone consists of machine learning models. They process both structured and unstructured data to discover patterns that human analysts cannot see at all. These models take input from many sources such as customer interactions, market research, competitor analysis, production metrics, and quality control systems. Together, they provide companies with actionable insights.
Natural language processing technology allows teams to scale up their analysis easily. Teams extract whole meanings from customers’ opinions, support tickets, social media conversations, and survey responses through AI processing. An AI product manager can analyze 500K comments from customers in just 12 minutes. A human team needs 3 months for this. The manager will extract the top 15 feature requests with 94% accuracy. Computer vision systems perform several tasks. They assess the aesthetics of a design, spot manufacturing flaws of less than 0.3mm, and even see through users’ eyes. Video study shows how they cope with physical products.
Generative AI has brought a revolution in the ideation and design stages. Tools based on generative algorithms can generate 200 distinct product variations within one hour. They follow technical specifications, market limitations, and brand guidelines. Not one of them would be a mere random iteration. They would be solutions that teams optimize considering manufacturing feasibility, cost targets, and user preferences all at once. Medical companies that employed generative AI in healthcare product development cut down the time needed for prototype iteration cycles. The reduction went from 14 weeks to just 8 days. At the same time they improved their regulatory compliance scores by 41%.
How Predictive Analytics Powers Product Success
Predictive analytics engines anticipate the future of the product, the market, and even the places where it might fail before teams create physical prototypes. They predict with an accuracy of 76-83%. This is dramatically higher than the expert human predictions of 34%. They rely on historical product data, current market conditions, and emerging trends. Real-time data pipelines based on Apache Kafka and Azure Stream Analytics work in such a way that decision-makers receive insights almost as soon as teams generate data. They don’t wait for months after quarterly reports are published.
What Role Do AI Play in Ideation, Design, Prototyping, and Testing Stages Throughout the Process?
The ideation phase is the one where AI’s pattern recognition abilities are utilized to the greatest extent. AI tools for product designers scan not only patent databases but also academic research, competitor product launches, and consumer trend data. They find areas of opportunity. One manufacturer in the consumer electronics sector utilized AI-backed ideation tools. They looked through 3.7 million product reviews and 840 patents. They unearthed a $230 million market segment that was undeveloped. Traditional market research techniques completely missed it.
In the design stage, AI in design workflows speed up the iteration process with the help of generative algorithms. These create optimized solutions according to engineering constraints and user requirements. One company that manufactures aerospace components managed to cut the time needed for designing complex parts. The reduction went from 6 weeks to 4 days by employing topology optimization algorithms. AI generated designs that were 23% lighter and 31% stronger than the ones designers created. They required 18% less material. Product designers are not only using these systems but also giving them creative direction while the AI takes care of computational optimization.
From Linear Bottleneck to Parallel Processing
Prototyping is no longer a linear bottleneck solution but a parallel process. Using digital twin technology, teams can perform thousands of tests at the same time. In the automotive industry, engineers are shifting to AI-powered simulation. A virtual model can go through 10 million miles of simulated driving covering all conditions: weather and road within 72 hours. That way, teams expose the whole reality of critical failure modes instead of waiting months for physical testing.
Testing procedures turn into predictive rather than reactive. AI business solutions take patterns from beta tests and early adopters. They predict how different user segments will interact with the product when teams finally make it available at larger scale. Machine learning models that are based on historical testing data can be 81% accurate. They predict which product features will cause support issues. This allows teams to fix them before general release. One SaaS company that used AI-based predictive testing frameworks saw a 68% reduction in post-launch critical bugs.
How Do AI Models and Data Pipelines Work Behind Intelligent Product Development Systems?
The technical structure of AI in product development systems revolves around three connected components: data gathering layers, model training environments, and decision support interfaces. Data from various sources flows into centralized data lakes. These sources include customer relationship management systems, IoT sensors, manufacturing equipment, market research, and social listening tools. Teams build these lakes on platforms such as Azure Data Lake or AWS S3.
Real-time stream processing engines are responsible for the initial filtering and transformation of data. They indirectly communicate this to machine learning algorithms. On average, the AI product development pipeline uses up to 15-40 terabytes of data every day. Teams extract features that predict product success metrics. Some of these features are customer sentiment scores, competitive positioning indices, technical feasibility ratings, manufacturing complexity scores, and market demand indicators.
Teams use distributed computing clusters for model training. They choose frameworks between TensorFlow or PyTorch. Ensemble methods that coordinate gradient boosting machines, neural networks, and random forests for AI product optimization tasks are usually 12-19% better than single-algorithm approaches. If it is a case of retraining the model whenever new data comes in teams might retrain a recommendation model every 6 hours. This keeps up with the latest market signals.
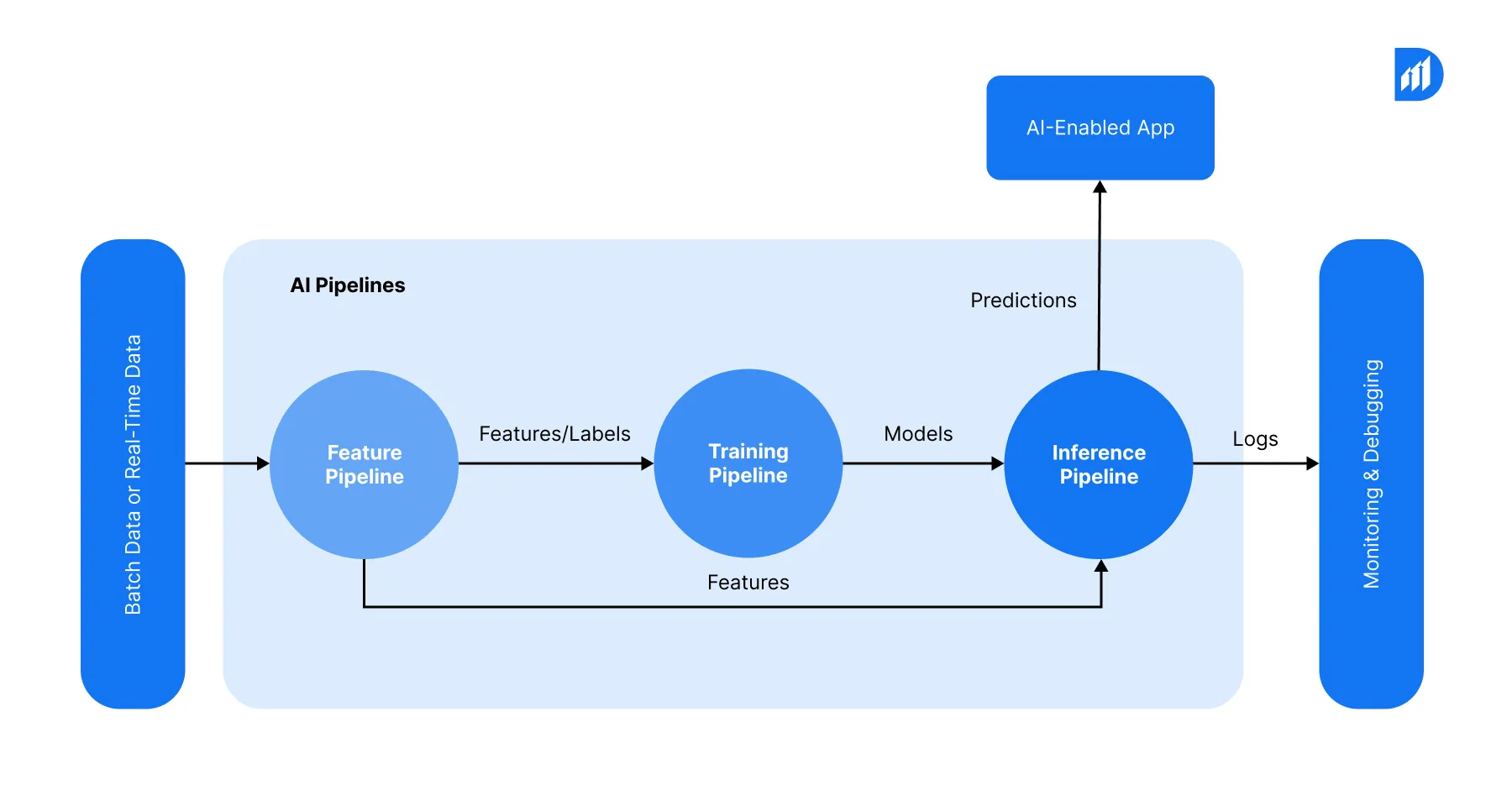
Real-Time Decision Support Through API Integration
The inference layer passes on predictions through APIs. Presently integrated, these tools work alongside, and even in combination, with the prominent product management software like Jira, Azure DevOps, or even home-built dashboards. When a product manager evaluates a feature suggestion, the application is capable of getting an elaborate impact analysis done in no more than 2 seconds. This includes likely adoption rate, cost of development estimate, score of competitive differentiation, and rating of manufacturing complexity. This study is based on 200+ data sources and involves 14 distinct prediction models running concurrently.
AI and ML solutions in a production setting come with the necessity of really good monitoring and feedback loops. Teams continuously track model performance metrics, prediction accuracy, latency, data drift, and business impact. If a model drops its accuracy below a certain level (usually it is 75% for product feature predictions), the system automatically retrains it. The latest data becomes the source. Thus, the continuous improvement cycle guarantees the system’s gradual ascent in accuracy. It doesn’t gradually decline keeping pace with changes in market conditions.
What Real-World Use Cases Are Out There That Show the Significance of AI in Product Development?
A surgical instruments manufacturer for the medical industry employed AI-augmented design systems. They produced next-generation surgical instruments. The AI processed data from 2.4 million surgical procedure videos. It pointed out ergonomic changes that led to 37% reduction in surgeon fatigue during long operations. The generative design system offered 340 instrument ranges of great hand size and surgical specialty compatibility. Clinical tests reported a 28% increase in time-saving. They showed a 41% decrease in complaints regarding ergonomics in comparison to traditional instrument-making.
A brake component maker who works with the automotive industry benefitted from AI-enabled materials science algorithms. They came up with lightweight brake parts. The program was able to study the molecular structure of 12,000 material compounds. It predicted the performance of different materials under 500,000 stress situations. Teams simulated these situations. Among the identified materials was an alloy mixture that not only cut component weight by 19% but also increased heat dissipation by 34%. The traditional way of research on materials would take about 4-6 years of lab testing. In 11 months, the AI product development approach resulted in $2.7 million reduced R&D cost.
AI-Powered Feedback Loops in Beta Testing
A consumer electronics company provided artificial intelligence in the form of an AI-powered chatbot during the product’s beta testing. They gathered structured feedback from 50,000 users at the same time. The AI examined the dialogues, marked 87 different usability problems, and organized them according to frequency and seriousness. Product teams received daily updates on features that caused user confusion, features that created positive feeling, and features that users didn’t frequently use. Teams created a communication channel between development and customer support. The duration for recognizing problems and realizing fixes dropped from 3 weeks to 4 days.
The furniture producer resorted to computer vision AI. They made the best possible use of factory size and production methods. The system scrutinized sweeps of video taken at the production area. It was able to point to areas where teams cut production rate down by 15%. It made a total of 23 changes to the factory layout and foretold their impact via simulation. Following the renovation, production capacity increased by 31%. Teams added no extra machinery or personnel. The rate of defects fell by 44%. The AI has identified the flaws in quality control which the human supervisors were not able to catch over the years.
What Types of AI Solutions and Tools Are Used in Product Development Workflows?
Product design AI tools are divided into several categories. Each category caters to a certain need in the process. For instance, generative design software like Autodesk Fusion 360 or nTopology applies the use of topology optimization algorithms.
They produce designs that are structurally very strong yet very light. These devices minimize the material used in the process by as much as 20-40%. The performance characteristics are either kept or even improved. Design teams specify limitations such as weight limits, stress requirements, and production methods. The AI in return presents hundreds of viable solutions in a matter of hours.
Natural language processing-enabled market intelligence systems monitor competitor activities, consumer attitudes, and the rise of new trends. They examine 200+ sources. Taking Crayon or Kompyte as examples, these tools automatically track the moves of competitors in terms of product releases, price adjustments, and marketing activities. AI product manager groups receive these observations. Based on the data collected, the roadmap decisions are made by them. Through AI market analysis, a B2B software company was able to spot a pricing flaw in one of its competitors. Consequently, the company repositioned its product. This led to a 34% gain in the win ratio of competitive deals.
Visual Innovation Through AI Image Generation
AI image generation services have made a huge impact on designers’ capability to communicate their product ideas to stakeholders through physical prototypes. By using Midjourney, DALL-E, and Stable Diffusion, designers may create lifelike product images based on textual description in a matter of minutes. A company that produces consumer goods employed AI image generation. They produced 500 different packaging design options for A/B testing with groups of consumers. This method turned out to be 87% cheaper than working with a traditional design agency. It also shortened the time from concept to testing from 8 weeks to 5 days.
To perform product testing, teams apply computer vision and machine learning. These are the primary techniques used in quality assurance tools. Companies providing such services like Applitools or test.ai are employing visual AI technology. They detect UI discrepancies for different devices as well as screen sizes. Mobile app developers using AI-based testing have reported experiencing a reduction of 60% in QA time. They experience a reduction of 45% in the number of bugs post-release compared to manual testing, which teams do through the traditional approach.
Classifying AI SaaS Products for Product Development
When teams evaluate AI SaaS product classification criteria, they look at several factors. These include deployment model, integration capability, scalability, and pricing structure. Cloud-based AI product solutions offer flexibility that on-premise systems can’t match. Teams assess whether the tool supports API integration, handles real-time data processing, and scales with growing product portfolios. Classification also depends on the specific use case whether it’s for design automation, market analysis, quality control, or predictive testing.
Most AI business solutions in the SaaS category follow subscription-based pricing. They range from $2,000 monthly for small teams to $50,000+ for enterprise deployments. The classification framework helps product teams match tools to their specific needs. For instance, a startup might need lightweight AI image generation services for concept visualization. A Fortune 500 manufacturer requires enterprise-grade systems with advanced security and compliance features.
In What Way Does AI Enhance Speed, Accuracy, and Cost-Efficiency in Comparison to Traditional Methods of Product Development?
The increasing speed of AI in product development is caused by the parallelization and automation of tasks. Teams have usually done these sequentially. The average concept-to-launch timeline of traditional methods is 12-18 months for a physical product and 6-9 months for a digital one. Companies that prefer AI methods to support their product development can shorten these periods by 40-55%. Teams perform market analysis, design optimization, and testing simulations simultaneously instead of doing them one after another.
Teams see the enhancement of accuracy in various aspects. AI demand forecasting cuts inventory mismatches by 35-42% in comparison to conventional forecasting methods. Product development teams are able to make better decisions regarding feature prioritization when AI examines actual user behavior patterns. This is better than relying on stated preferences in surveys. Research has shown these align with actual behavior only 23% of the time.
Cost efficiency is the outcome of waste elimination, faster process and resource allocation. Teams morph prototyping costs by 65-70% when designers through AI-powered digital twins detect design faults beforehand. They skip the physical models creating process. The company that forecasts consumer appliances in the market before they manufacture them came up with an idea. They used simulation-based testing for 80% of validation scenarios. This led to the reduction of prototype iteration costs from $340,000 down to $95,000 per product line. This is already a great cost saver that the company is banking on.
Compound Effects of AI Integration Over Time
The total impact of these enhancements does not become less dramatic as time goes on. An AI business solutions analysis of 200 product development teams showed that organizations with mature AI integration ship 3.2 times more products annually. They do this with 45% smaller development teams compared to the old ways. Teams generally realize ROI in about 6-9 months after implementation. During these times, the organization will enjoy a 30-40% cost cutting per product development cycle.
What Are the Latest Trends and Innovations Shaping AI in Product Development?
Teams’ communication of product requirements is definitely redefined by multimodal AI systems. These blend text, image, and voice inputs. Instead of putting down in writing parts that would go into a specification document, product managers can easily have a rough drawing representing the concept. They explain the function and let AI make the technical specifications and user stories that are inclusive and elaborate. This practice takes the requirement documentation time down by 75%. At the same time the clarity improves while the chances of misinterpretation decrease.
The move to autonomous design agents marks the next step of artificial intelligence in AI in product development. Rather than making the designers’ work easier, these systems, by their very nature, completely take over the design process. They decide what is best, switch between options, and come up with unique ideas. An MIT researcher group once realized the independent design operator. It produced a bike frame draft about 12% lighter and 23% more aerodynamic than any frame a human designed in the last 50 years.
Real-Time AI Collaboration in Product Planning
The interaction between AI systems and human teams in real-time is getting more elaborate every day. The cutting-edge AI product manager tools now, besides attending product planning meetings, also do the analysis of discussions going on in real-time. They bring up related market data, point out possible technical restrictions, and propose different ways based on historical success patterns. This change in AI’s role moves it from just being a tool to one that acts as a collaborator who gives valuable input.
Placing AI at the edge allows teams to do testing and optimization of products on devices instead of on the cloud. This allows for product analytics that do not compromise privacy. User behavior analysis takes place on smartphones or IoT devices, thus keeping it local. Companies get better behavioral data while they are still respecting users’ privacy. This, in turn, solves the problem of 73% of consumers who claim that privacy issues are among the factors that make them less willing to provide product feedback.
How is Durapid Backing Up Companies in the Assimilation of AI into Product Development Systems of the Enterprise?
Durapid Technologies is involved in the process of implementing full AI in product development workflow. The assistance comes through custom solution architecture and integration services. Our team consists of more than 150 professionals certified by Microsoft and more than 95 consultants certified by Databricks. They design AI pipelines that link current product management tools with machine-learning platforms like Azure ML, AWS SageMaker, and Databricks.
We are experts in constructing the data foundation that is needed for AI product development to scale. This encompasses real-time data collection from customer interaction points. It includes ETL processes that convert raw data to features suitable for ML. It also includes model deployment infrastructures that are responsible for integrating predictions into existing product workflow. Our implementation of the AI-based product analytics platform for a healthcare technology client has been one of the remarkable stories. It led to the reduction of client product iteration by 52%. At the same time, it increased feature adoption rates by 34%.
By solving exclusively the product development bottlenecks, we offer a solution that is different from merely employing AI tools. We carry out a very thorough analysis of the workflow in order to locate points where AI is most beneficial. This could be in the areas of market intelligence, design, quality prediction, or demand forecasting. This meticulous method not only gives returns on investments that teams can measure in the first quarter of deployment. It simultaneously creates the conditions for a longer-term change in the organization.
Durapid collaborates with Microsoft, SAP, and the major cloud platforms. Thus, clients can enjoy the most advanced AI features and the best IT infrastructure in the industry. Our co-selling arrangement with Microsoft provides the opportunity of getting first-rate access to Azure OpenAI services, cutting-edge analytics tools, and tech support. This hastens deployment time by 30-40% when compared to usual deployment methods.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is AI in product development and how does it work?
AI in product development uses machine learning, NLP, and computer vision across the entire cycle from ideation to manufacturing to gather data, foresee results, and automate decisions with 76-89% accuracy.
Which industries benefit most from AI in product development?
Healthcare, automotive, consumer electronics, and manufacturing industries experience the biggest gains with development cycles shortened by 40-55% and product costs saved by 30-40%.
What is the price range for AI implementation in product development?
Implementation costs vary from $150,000 to $800,000 depending on scale, with typical ROI realized in 6-9 months through savings in prototyping and quicker time-to-market.
What are the AI-enabled tools for product teams?
Teams often use Autodesk Fusion 360 for generative design, Azure ML or AWS SageMaker for predictive analytics, and Databricks for data pipeline management.
Are smaller companies allowed to use AI in product development?
Yes, SaaS solutions and cloud-based AI tools let small teams access enterprise-grade capabilities starting at $2,000-5,000 monthly with usage-based pricing that grows proportionately.
Deepesh Jain is the CEO & Co-Founder of Durapid Technologies, a Microsoft Data & AI Partner, where he helps enterprises turn GenAI, Azure, Microsoft Copilot, and modern data engineering/analytics into real business outcomes through secure, scalable, production-ready systems, backed by 15+ years of execution-led experience across digital transformation, BI, cloud migration, big data strategies, agile delivery, CI/CD, and automation, with a clear belief that the right technology, when embedded into business processes with care, lifts productivity and builds sustainable growth.





