AI Agents vs AI Assistants vs Bots: Which Intelligence Does Your Business Actually Need?
Three years ago, a global logistics company deployed what they called an “AI solution” to handle customer inquiries. Currently their system needs human help to process 68 percent of customer requests. It costs $340,000 to maintain each year. Their customer satisfaction rating has decreased by 14 points. The company development staff selected inappropriate AI technology for AI in product development work because they failed to understand their actual requirements. People need to know about AI agents and AI assistants and chatbots. Their understanding helps businesses decide which AI investment will bring 10x return or turn into another unsuccessful digital transformation initiative.
The correct AI architecture enables companies to achieve 47 percent faster issue resolution and 31 percent lower operational expenses. This compares to businesses that select technology incorrectly according to their operational needs (Gartner, 2024). The guide presents detailed explanations of each technology’s functions and appropriate usage situations. It also covers the financial impact of making incorrect decisions which costs businesses $1.2 million annually through resource waste and lost chances. Organizations are increasingly exploring generative ai to power their next-generation systems.
What is a Chatbot?
A chatbot is a software program that uses rules to create automated conversations. It follows its specific scripted material and decision-making paths. Traditional chatbot systems use if-then logic. Users input certain keywords or phrases which trigger the bot to deliver standard responses from its established knowledge base. The systems perform best when they handle numerous identical questions which follow a fixed conversation route. A retail chatbot responds to “What are your store hours?” and “Where’s my order?” inquiries. It receives these thousands of times throughout the day with the same answer. This technology uses pattern matching and keyword recognition to identify patterns. It cannot understand the actual meaning behind what people say. Many businesses now complement these basic systems with AI and ML solutions for enhanced capabilities. Modern chatbots use natural language processing (NLP) capabilities instead of basic keyword triggers.
However, their primary constraint prevents them from learning any new information beyond what their initial development taught. The system transfers client requests which have not received approval to human representatives. Traditional chatbots in the industry achieve successful customer inquiry resolution through automated systems at a rate between 35 to 40 percent. Forrester Research from 2024 shows the remaining customer inquiries which they handle require human intervention. Companies deploying AI powered chatbot systems see better resolution rates. The system follows a simple flow which starts with user input and ends with a programmed response. This results from keyword matching and database searching.
The simple design of chatbots enables businesses to implement them at low costs which range from $5,000 to $50,000 based on their specific needs. The maintenance expenses increase because businesses have to manually modify scripts. They do this whenever new products and policies or new scenarios emerge. This method demands constant developer involvement which results in market response delays that last several weeks. Healthcare organizations exploring generative AI in healthcare often start with basic chatbots before advancing to more sophisticated AI assistants.
How Chatbots Work?
Chatbots operate using a three-step system which converts user input into responses that can be executed. This process starts when users submit their queries through the messaging interface. The system can be accessed through a website widget, a mobile application or a messaging platform which includes WhatsApp and Slack. The system first processes input through a natural language understanding (NLU) layer. This process identifies words and phrases to separate text into distinct linguistic components. Basic chatbots use regular expressions and keyword matching. The system initiates the password reset process when users input “password reset” into the system.
More advanced systems use intent classification models. Educational institutions develop these with their labeled datasets. They sort user requests into predetermined categories which include “account_help,” “product_inquiry,” and “billing_question.” The chatbot uses its knowledge base to identify user intent. This consists of structured databases and JSON files that store response templates. After that, the system retrieves the corresponding answer. The natural language generation (NLG) component transforms it into conversational text.
Basic bots deliver fixed messages. Sophisticated systems use template-based response generation to create customized answers. These use customer information from their CRM databases and other databases. The conversation proceeds according to a state machine model. User input causes the system to change states. It moves from greeting through intent identification and information gathering to resolution. When the bot cannot determine user intent between 70 percent and 75 percent accuracy, it uses human support.
Integration and Deployment
The chatbot establishes connections to backend systems through API-based integration methods. The banking chatbot enables users to check their account balances. It does this through REST API requests that it sends to the bank’s core systems. The system determines which integrations to use during the development phase.
What is an AI Assistant?

An AI assistant functions as a smart software program which operates through its machine learning and natural language processing capabilities to process contextual information while learning from user interactions and performing tasks in various fields. The system operates without the need for dedicated programming to handle every specific use case. AI assistants use large language models (LLMs) and contextual reasoning to understand user requests. The system requires them to determine user intent when users create ambiguous or conversational or novel requests. The core distinction between two things exists through their ability to adapt and their capacity to comprehend. The virtual assistants Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant provide correct answers.
They use their ability to understand language and their access to knowledge graphs to deduce the answer to unknown questions. An AI application assistant in AI in product development allows teams to access product specifications and user feedback. They generate insights through natural language queries instead of learning complex query languages or using different databases. Healthcare providers also benefit from an ai health assistant for clinical decision support.
How AI Assistants Support Different Industries
The systems keep track of both past conversations and current user information throughout different interaction periods. The AI assistant remembers your past inquiry about quarterly sales data from yesterday. It uses that information to assist with your current request “Show me the regional breakdown.” This ability to understand current situations drives results. An ai virtual assistant in healthcare streamlines patient data retrieval for medical staff. The system foundation combines five AI functionalities. These include speech recognition for voice commands, natural language processing to determine user intent, and knowledge acquisition from multiple data sources. Cognitive systems solve complex problems through natural language generation to produce human-like answers. Microsoft Azure OpenAI Service, Amazon Bedrock, and Google Vertex AI represent three major platforms. They deliver businesses the essential tools for developing customized AI assistants which meet their particular operational requirements.
Enterprise AI assistants use APIs and connectors to connect with internal systems.Data retrieval occurs through ERP platforms combined with CRM systems and document repositories and analytics tools. The dedicated team for AI in product development needs to access CAD files from Autodesk Fusion 360 and user research data from Qualtrics and market research data from Salesforce. The system retrieves regulatory requirements from compliance databases. All this happens in response to a single natural language query like “What compliance issues could delay our Q3 product launch?” Sales teams leverage salesforce ai sales assistant capabilities to accelerate their workflows.
What are AI Agents?
AI agents are like team members who do not wait for instructions. They work independently within set limits, spot problems, plan multi-step actions, and keep processes moving without constant human input, unlike AI assistants that mostly respond when asked. From tracking tickets and creating bug reports to optimizing inventory and updating customers automatically, AI agents quietly handle goals in the background and help teams launch faster with far less coordination effort.
Core Architecture of AI Agents
The technical architecture consists of three components. These include perception modules that gather data from various input sources and reasoning engines that assess present conditions against objectives. Planning components create action sequences. Execution layers utilize system components to implement decisions. Advanced implementations use multi-agent systems where specialized agents collaborate. A procurement agent coordinates with inventory agents, demand forecasting agents, and supplier relationship agents to optimize supply chain performance.
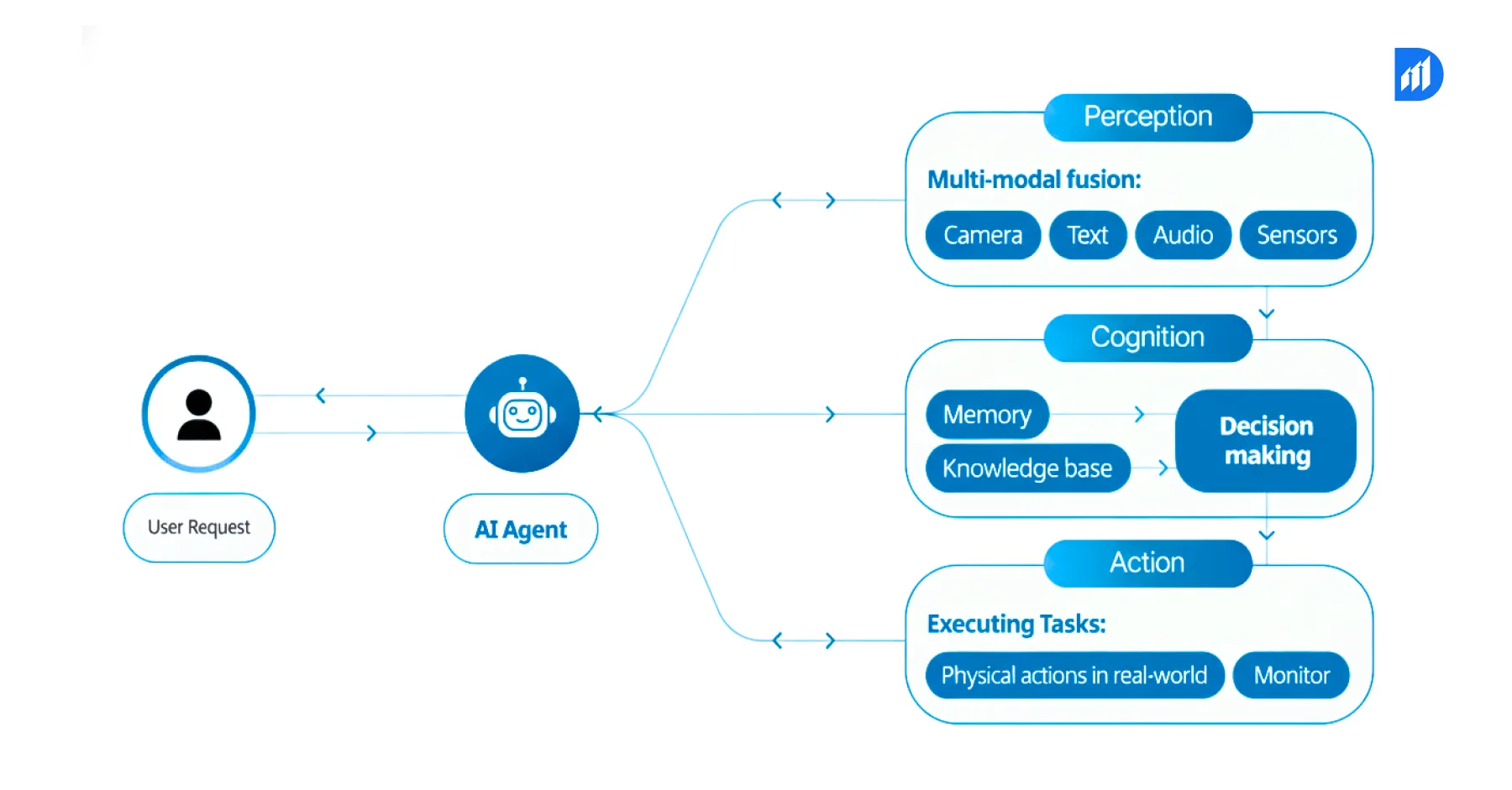
AI agents can be developed through modern frameworks. These include Microsoft Semantic Kernel and LangChain and AutoGPT. They create reasoning systems that use generative AI while accessing enterprise systems and data repositories. These platforms establish orchestration layers which handle the complete agent lifecycle. They control the interaction between multiple agents. They make sure that actions comply with established business rules and governance standards.
Growth of Agentic AI Companies
The shift from reactive assistance to proactive agency explains something important. Companies implementing AI agents see 3.5x higher return on AI in product development investments compared to those using only chatbots or assistants (Gartner, 2024). Major agentic AI companies have emerged to address this demand.
Recent agentic ai news highlights how organizations are deploying autonomous systems at scale. Specialized providers like agentic ai pindrop anonybit use agentic AI for voice authentication and identity verification respectively. Contact centers deploy ai voice agent systems to handle complex customer interactions that traditional chatbots cannot manage. The system needs proper supervision. Artificial intelligence agents require complete observation and exact working limits. They need emergency shutdown systems to avoid creating unexpected results while they operate without human control.
Chatbot vs AI Assistants vs AI Agents vs Agentic AI: Key Differences
Technical differences between chatbots, AI assistants, AI agents, and agentic AI quietly decide how much real value a business actually gets from AI in product development. The design of chatbots limits their capabilities to handle one question at a time while requiring human intervention for system updates. AI assistants use their understanding of context to learn from user interactions and handle complex dialogues. AI agents show advanced capabilities because they create objectives and execute their plans while they keep improving their decision-making process. Agentic AI functions at its most advanced level through its ability to create independent strategies and acquire knowledge from its experiences while it solves difficult challenges with limited human assistance.
With every tier, abilities grow, learning becomes stronger, and human supervision reduces. Costs and deployment time rise alongside this growth, but so does accuracy and long-term impact. Chatbots are quick and affordable to deploy through cloud bot services. AI assistants rely on LLM platforms and take moderate time and budget. AI agents need advanced frameworks and higher investment. The development of Agentic AI needs specific orchestration and MLOps pipelines but delivers optimal strategic alignment and operational performance. The main decision requires organizations to select between two business goals instead of choosing between different technological options.
High-volume standard queries work best with chatbots. AI assistants naturally support two functions which include information retrieval and task assistance. AI agents use their capabilities to automate operations and optimize processes beforehand. Agentic AI systems support both strategic forecasting and large-scale planning activities. The best solution requires an organization to select a system which meets its present requirements while providing future expansion possibilities.
Understanding Agentic AI
Agentic AI describes advanced systems which create their own subgoals and build strategies. They change their methods based on outside factors. While chatbots and AI agents execute fixed tasks, agentic AI systems use self-governing methods. They modify their objectives when they perceive new environmental changes. A supply chain agentic AI might shift from cost optimization to resilience maximization. This happens when detecting early indicators of supplier instability, without waiting for human direction. Monitoring agentic ai news keeps businesses informed about latest developments in this space.
Which AI Tool is Right for You?
Your business requirements should determine which AI technology to use for AI in product development. Its capabilities should meet your essential needs instead of selecting the highest level technology. The decision framework centers on three factors: task complexity, required autonomy, and acceptable risk tolerance.
When to Deploy Chatbots
Chatbots should handle high-volume repetitive queries when the questions follow expected patterns. Customer service scenarios where 70% of inquiries fall into 10-15 categories make ideal chatbot applications. Customers who use telecom services to check data usage or pay bills or report outages will achieve 92% success through chatbots. These charge $0.08 per interaction compared to $6.50 for human agents (Forrester 2024). The breakeven point typically arrives after processing 50,000 monthly interactions. The return on investment increases when the interaction volume between customers and businesses grows.
When to Choose AI Assistants
AI assistants help users when they need to explain information across multiple situations. These situations need them to connect separate pieces of information. Product development teams asking questions like “Which customer segments rated the checkout flow below 3 stars?” benefit from this. Teams asking “Compare feature adoption rates between premium and free tiers” also benefit. AI in product development assisted workflows understand their needs through multiple data sources. Organizations experience a 63% decrease in information search time. Their decision-making processes become 41% faster after they implement AI application assistant systems (McKinsey 2024). Implementation becomes necessary when knowledge workers dedicate more than 15 hours each week to searching information. This happens across multiple unlinked systems.
When to Implement AI Agents
AI agents should be deployed during process work that needs both extended time operations and permanent system supervision. They also need system adjustments to handle all environmental changes. Manufacturing quality control scenarios where best ai agents monitor sensor data show this well. They detect anomalies, adjust machine parameters, and alert operators only for exceptions. These deliver 67% reduction in defect rates and $2.3M annual savings for mid-sized facilities (Gartner, 2024). The investment justifies itself when manual process monitoring costs exceed $200,000 annually. Response delays that cause measurable business impact also justify the investment. Emerging agentic ai companies continue to innovate in this domain.
When to Consider Agentic AI
Agentic AI functions better when strategic tasks need machines to independently optimize multiple changing objectives. Demand forecasting systems that analyze market trends, competitor actions, and supply chain constraints exemplify this category. They also analyze customer behavior to dynamically adjust production schedules and pricing strategies. Early adopters report 23% improvement in forecast accuracy and 18% reduction in inventory carrying costs. This translates to $4-7M annual impact for billion-dollar revenue businesses (McKinsey, 2025).
Risk Assessment in AI Selection
Companies need to assess their risk tolerance before making decisions. Chatbots carry minimal risk. Incorrect answers frustrate customers but rarely cause material harm. Organizations need to monitor AI agents which make purchasing decisions and production schedule changes. These systems create high-stakes operational risks. Organizations should start with low-risk applications which need system monitoring. They should develop system trust before they improve their existing processes. A phased development approach works best for AI in product development. This includes initial chatbot development for frequently asked questions. It includes subsequent development of an AI assistant for internal knowledge and an AI agent for specific workflows.
What Should Businesses Consider When Selecting AI Agents or Chatbots?
The implementation of artificial intelligence solutions succeeds when organizations achieve their business goals. This happens through proper alignment with the required AI capabilities for AI in product development. The selection process should evaluate six critical dimensions before committing resources to development and deployment.
Integration Complexity
The complexity of integration procedures determines both the overall asset expenses and the duration required to achieve operational efficiency. Organizations can implement chatbots which require API links to their FAQ databases and ticketing systems. This happens within a four to six week period without needing significant system modifications. AI agents which require access to ERP systems and customer databases need more time. They also need access to supply chain platforms and analytics tools.
These need four to six months for their integration process along with continuous maintenance. Organizations should conduct audits of their present system APIs. They should examine their data accessibility options and security prerequisites before they begin to calculate their implementation timeline. Companies which fail to comprehend integration difficulties experience project delays. These extend 137 percent beyond their original time estimates. This comes from Forrester research conducted in 2024.
Data Quality and Availability
Data quality and availability constrain AI effectiveness regardless of algorithmic sophistication. AI assistants in AI in product development require structured access to user research, feature specifications, market data, and performance metrics. The process of cleaning and structuring information will use 60 to 70 percent of implementation resources. This happens when the required data exists in 15 different systems which use multiple inconsistent formats. Organizations should assess data readiness using a maturity framework.
Ask these questions: Is data centralized? Is it labeled and structured? Does it cover the required domain? Can systems access it in real-time? Low data maturity necessitates infrastructure investment before AI implementation delivers value.
Human Oversight Requirements
Organizations develop their operational frameworks through monitoring requirements which need to be checked by human beings. Chatbots need minimal monitoring beyond periodic script updates. Autonomous AI systems require organizations to develop three essential components. These include escalation procedures and exception handling protocols and monitoring systems. Organizations should define decision boundaries.
Which actions can AI take independently? What requires human approval? How quickly must humans respond to exceptions? Companies that use AI systems without proper governance frameworks face incident rates which are 3.2 times higher. Their resolution times take 58 percent longer. This comes from Gartner research from 2024.
Scalability and Cost Trajectory
Different AI systems show completely different patterns of growth and operational expenses. Chatbot costs scale linearly with conversation volume and remain predictable. AI assistant costs increase with additional data sources and user base growth. They reach a maximum when infrastructure costs are distributed over time. AI agent operational costs depend on system integrations and action frequency. This creates a risk of non-linear cost increases when the system design is inadequate.
Organizations should model costs at 10x, 50x, and 100x current usage volumes. Account for API calls, compute resources, storage, and human oversight. Cloud-native architectures using Azure OpenAI Service or AWS Bedrock provide flexible scaling. They require careful monitoring to avoid runaway costs.
Regulatory and Compliance Constraints
AI systems face complete operational restrictions in regulated industries. This happens because of legal and compliance requirements. Healthcare AI assistants need to follow HIPAA regulations which mandate specific security controls and audit trails. These protect patient data. Financial services AI systems that execute trades need to follow SEC regulations. These require their decision-making processes to be transparent.
Organizations in regulated sectors should involve compliance teams early. Document AI decision logic, implement audit capabilities, and establish human-in-the-loop controls for high-stakes actions. An ai health assistant must comply with all relevant healthcare data protection laws.
Internal Expertise and Change Management
The success of AI investments depends on internal expertise combined with effective change management practices. Chatbot deployment needs minimal user training. Customer service teams must use their skills to resolve customer issues. Users need to learn how to create effective prompts for AI assistants. These require trust development through value demonstrations. AI agents need teams to change their work approach from task execution toward exception management and agent performance optimization.
Organizations should assess current AI literacy, plan training programs, identify champions, and create feedback loops for continuous improvement. Organizations that implement change management together with technology investments achieve 2.4 times greater user adoption. They experience 67 percent quicker value realization. This comes from McKinsey research from 2024. AI assisted initiatives succeed when backed by proper training.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can AI agents completely replace human employees?
AI agents allow humans to maintain their work abilities because they handle repetitive work while humans perform judgment work and creative tasks and solve difficult issues.
How do chatbots handle requests outside their programming?
Chatbots use confidence thresholds to detect unfamiliar requests and escalate to human agents when confidence falls below 70-75%.
What’s the difference between AI assistants and virtual assistants like Siri?
Enterprise AI assistants integrate with business systems and use company-specific data while virtual assistants access general knowledge and personal device data. An ai application assistant offers deeper organizational integration.
Do AI agents need constant internet connectivity?
Most AI agents require internet access to leverage cloud-based LLMs and distributed data sources. Edge deployments exist for offline scenarios but involve higher costs.
How long before businesses see ROI from AI implementations?
Chatbots typically reach ROI within 6-9 months, AI assistants within 12-18 months, and AI agents within 18-24 months. Salesforce ai sales assistant implementations often show faster returns in sales environments.
Durapid Technologies specializes in developing AI solutions which match your business requirements through generative AI and AI and ML solutions that produce measurable results. Our 120 certified cloud consultants together with our 95 Databricks-certified professionals assist enterprises with their AI implementation needs. This applies regardless of whether they are starting their first AI-powered chatbot deployment or expanding their generative AI in healthcare systems. Contact us to discuss which AI approach aligns with your strategic objectives and delivers the 3-5x ROI your business demands.





